从零实现一个最简单的特里树,同时了解特里树的使用场景。
wiki:
In computer science, a trie, also called digital tree or prefix tree,[1] is a type of k-ary search tree, a tree data structure used for locating specific keys from within a set. These keys are most often strings, with links between nodes defined not by the entire key, but by individual characters. In order to access a key (to recover its value, change it, or remove it), the trie is traversed depth-first, following the links between nodes, which represent each character in the key.
Trie 树,也叫“字典树”。顾名思义,它是一个树形结构(n叉)。它是一种专门处理字符串匹配的数据结构,用来解决在一组字符串集合中快速查找某个字符串的问题。
Trie 树的本质,就是利用字符串之间的公共前缀,将重复的前缀合并在一起。
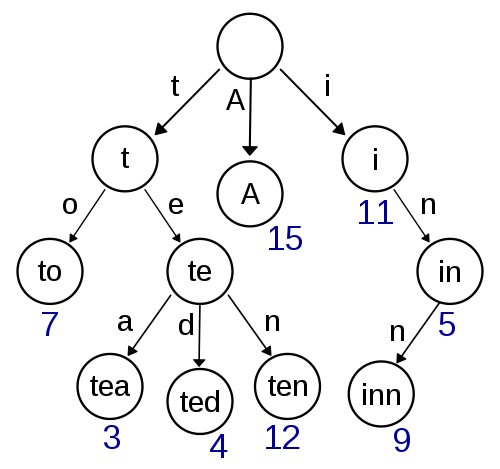
提供的功能包括:
- 插入新的单词
insert
- 查找单词是否匹配
find
限定只处理a-z26个小写字母组成的英文单词场景。
我们的节点 TrieNode26Char 表示特里树节点:
val表示当前节点值;TrieNode26Char[] children 则存储下层节点;
- 可以看到这种实现下如果某层节点不够满、前缀复用率不高,数组空置会比较严重,会浪费空间,这个是优化点;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
public class TrieNode26Char {
/**
* 当前节点值
*/
char val;
/**
* 子节点
*/
TrieNode26Char[] children;
/**
* 是否为一个单词末位
*/
boolean isEndingChar;
public TrieNode26Char(char val) {
this.val = val;
this.children = new TrieNode26Char[26];
}
}
|
关键操作#
插入单词与匹配单词串逻辑类似,均是沿着树往下层节点找,核心思想是dfs。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
|
public class TrieTree {
/**
* 根节点不存储val
*/
private final TrieNode26Char root = new TrieNode26Char('-');
public void insert(String word) {
insert(word.toCharArray());
}
public void insert(char[] word) {
TrieNode26Char curr = root;
for (int i = 0; i < word.length; i++) {
int iIdx = word[i] - 'a';
if (curr.children[iIdx] == null) {
curr.children[iIdx] = new TrieNode26Char(word[i]);
}
curr = curr.children[iIdx];
}
curr.isEndingChar = true;
}
public boolean find(String word) {
return find(word.toCharArray());
}
public boolean find(char[] word) {
TrieNode26Char curr = root;
for (char c : word) {
int idx = c - 'a';
if (curr.children[idx] == null) {
return false;
}
curr = curr.children[idx];
}
return curr.isEndingChar;
}
public void print() {
Deque<TrieNode26Char> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offerLast(root);
int level = 0;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
++level;
int size = queue.size();
System.out.print("第" + level + "层:");
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TrieNode26Char node = queue.pollFirst();
if (node == null) {
continue;
}
System.out.print(node.val + " ");
if (node.children != null) {
for (TrieNode26Char child : node.children) {
queue.offerLast(child);
}
}
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
|
复杂度分析#
查找、匹配单词复杂度只跟word长度有关,查一次最多遍历len(word)个节点。因此时间复杂度O(len(word))。
从根创建树的复杂度则取决于所有单词的长度,为O(n)。
按我们目前的最简实现,数组空间复杂度会比较高,特别是某层子节点只存了一个字符时,数组也需要开辟26的长度。
使用场景#
| pros |
cons |
| 1. 字符串中包含的字符集不能太大。 |
适用于查找前缀匹配的字符串(非精确搜索),如搜索提示。 |
| 2. 要求字符串的前缀重合比较多,不然空间消耗会变大很多。 |
|
| 3. 跳转结构,对CPU缓存不友好。 |
|
以上,实现了最简单的特里树,并且分析了复杂度,对比了场景优劣。
Ref#
