从零实现位图BitMap,使用实测数据感受其优劣,同时了解BitMap结构的使用场景。
wiki:
A bitmap is the data structure that immediately pops in your head when there’s a need to map boolean information for a huge domain into a compact representation. It is a very popular data structure whenever memory space is at a premium. OS kernels (memory pages, inodes, etc.), digital imaging, etc.
位图BitMap要点:
- 紧凑型存储,节约内存占用;
- 支持二值存储、读取;
话不多说,我们直接来写一个:
提供的功能包括:
BooleanArrayBitMap#
最直观的想法,当然是直接开辟一个boolean[]数组来表达每个下标下的boolean状态。
当然,事实证明,这个思路符合BitMap部分特征,如api一致,但是不够节省内存。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
|
public class BooleanArrayBitMap {
/*
* java语言中的boolean占一个字节
* 实测:
* 执行 333335874次set操作,共耗时:8170 ms
* BooleanArrayBitMap 10 亿容量 一共占用953.6743202209473 MB
*
* 而表达位图中的二值,仅需要一个位,即可
*/
/**
* 位图容量
*/
int capacity;
/**
* 存储数组
*/
boolean[] arr;
public BooleanArrayBitMap(int capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity;
this.arr = new boolean[capacity];
}
public void set(int i) {
assert i < capacity && i >= 0;
arr[i] = true;
}
public boolean get(int i) {
assert i < capacity && i >= 0;
return arr[i];
}
public void printMemoryInMB() {
System.out.println("BooleanArrayBitMap " + capacity / 100000000 + " 亿容量 一共占用" + MemoryUtils.byte2MB(capacity + 4) + " MB");
}
}
|
基于数组的简单封装,发现内存占用不少。Java的boolean占用1个字节,也就是8个bit位,而其实BitMap的二值只需一个位即可。
RealBitMap#
我们尝试用位操作来处理api。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
|
/**
* 真正基于位存储、操作的位图
*
* @author dragonsong @date 2022/7/14
* @see BooleanArrayBitMap 中基于boolean数组,一个boolean就占用一个字节,一个字节中有8位,对于表达二值其实有7位是浪费的
*/
public class RealBitMap {
/*
* 执行 333331423次set操作,共耗时:8762 ms
* RealBitMap 10 亿容量 一共占用29.802326202392578 MB
*
* 操作大致量级的set时,耗时与 BooleanArrayBitMap 接近,而内存占用却节省了 三十倍!
*/
/**
* 位图容量
*/
int capacity;
/**
* 存储数组
* char占用16位,一个char可表达16个二值
*/
char[] arr;
public RealBitMap(int capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity;
// capacity % 16 有余数才需要增加一个char存储
this.arr = new char[capacity % 16 == 0 ? capacity / 16 : capacity / 16 + 1];
}
public void set(int i) {
assert i < capacity && i >= 0;
// 商命中实际存储的数组下标
int quotient = i / 16;
// 余数命中实际操作的位
int remainder = i % 16;
// 将1存到 remainder 位置
arr[quotient] |= (1 << remainder);
}
public boolean get(int i) {
assert i < capacity && i >= 0;
// 商命中实际存储的数组下标
int quotient = i / 16;
// 余数命中实际操作的位
int remainder = i % 16;
return (arr[quotient] & (1 << remainder)) != 0;
}
public void printMemoryInMB() {
System.out.println("RealBitMap " + capacity / 100000000 + " 亿容量 一共占用" + MemoryUtils.byte2MB((double) arr.length / 2 + 4) + " MB");
}
}
|
RealBitMap在BooleanArrayBitMap基础上,仅仅修改为了用位操作数据的写入、读取。
复杂度分析#
set
一次位操作,O(1)get
一次位操作,O(1)range
遍历取决于入参范围,O(n)
看看十亿数据量级下的实测对比:
1
2
3
4
5
|
执行 333335874次set操作,共耗时:8170 ms
BooleanArrayBitMap 10 亿容量 一共占用953.6743202209473 MB
执行 333331423次set操作,共耗时:8762 ms
RealBitMap 10 亿容量 一共占用29.802326202392578 MB
|
操作大致相同量级的set时,RealBitMap与BooleanArrayBitMap耗时接近,而内存占用却节省了 三十倍!
| pros |
cons |
| CPU对位操作的优化,使得操作高效,读写性能接近数组寻址 |
数据量过小时,徒增了操作复杂度 |
| 极大节省内存占用 |
|
工业应用#
位图BitMap非常适合用在一些极大数据量但是内存宝贵、二值判断的场景。
并且结合一些变体,工业界有很好的应用。
二值操作#
如Redis中的位图。
Redis中的 SDS 支持位图操作。实现位于 bitops.c。
在一些比如上下班打卡、xx是否yyy(二值判断)的场景下,能以极低的内存开销完成功能。
BloomFilter#
基于BitMap+hash的概率型数据结构。
可用于判重、流量快速失败的场景。
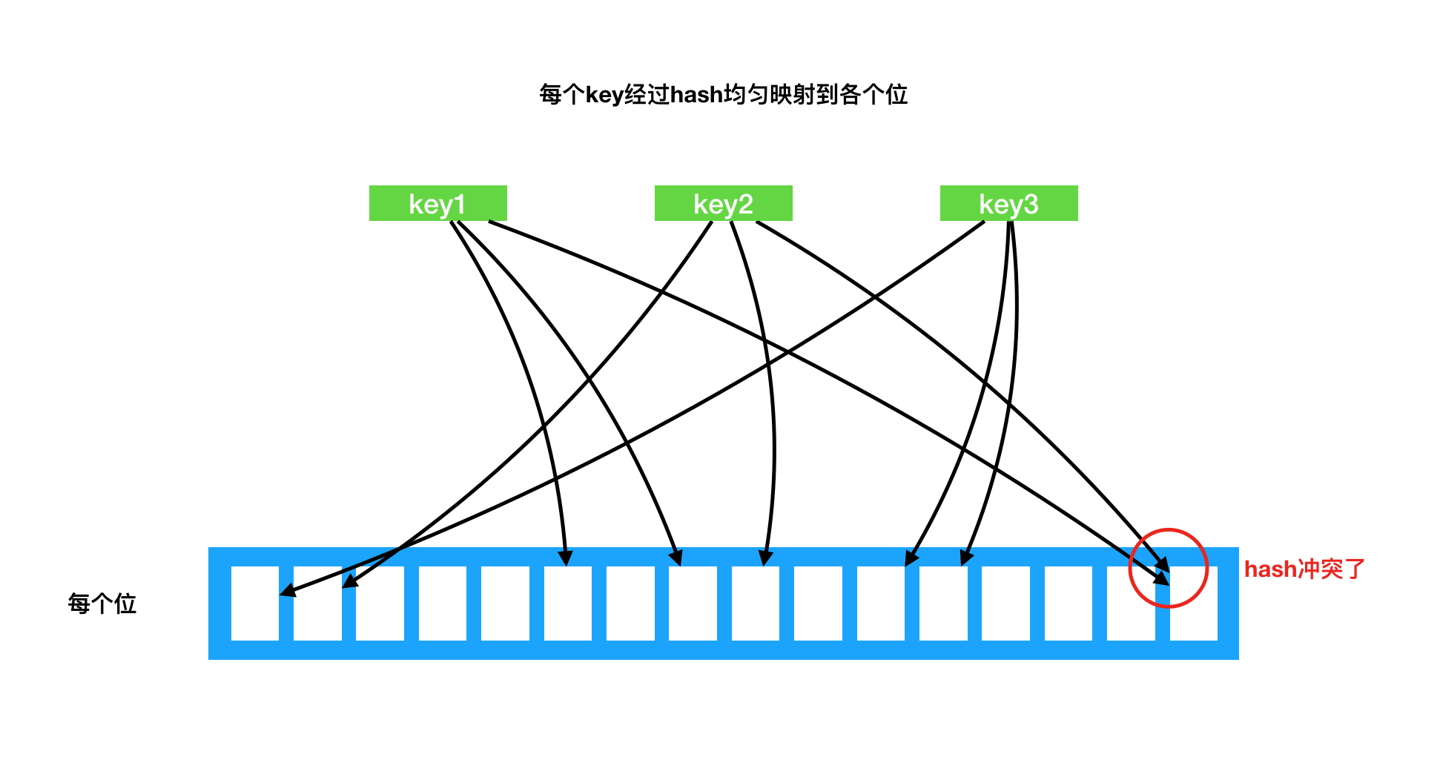
RoaringBitMap#
咆哮位图是另一个工业变体。
核心思路是不同数据量,底层使用不同的结构。
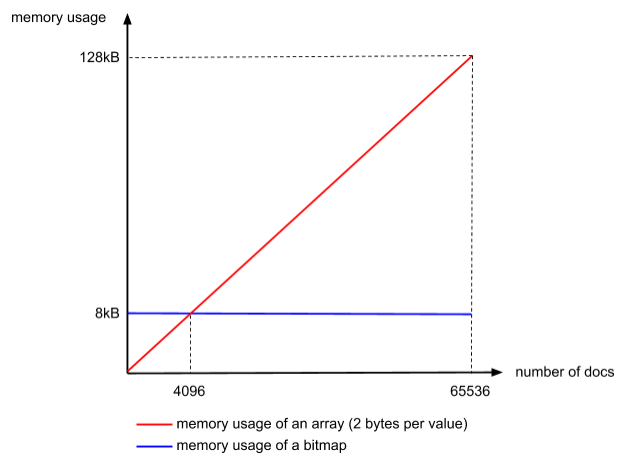
比如 简析ES/Lucene索引的基本设计原理 中也提到过Lucene底层在5版本之上就应用了 Daniel Lemire 的咆哮位图。关联Jira:LUCENE-5983。
以上,实现了最基本的位图BitMap结构,并且以实例对比了数值数组,输出了测试数据,列举了主流的工业应用场景。
Ref#

